When does sampling occur in GA?
Notion of sampling in web analytics
Something that in the past impacted a few number of large websites, sampling is now affecting many websites and web practitioners in their daily analytics experience. Indeed, with the ongoing digitalization, multiplication of touchpoints and development of complex measurement techniques, the number of recorded web interactions has just been exploding over the last years. Your website generates so much data that your web analytics tool needs to process a part of the larger data and extrapolate it in order to deliver you reports in a reasonable amount of time. That is what sampling refers to.
What is a hit?
Sampling in web analytics is tightly linked to the notion of hit. A hit is an interaction that results data being sent to your analytics tool. Technically, each time you code loads on a page, it will send data to a collection server. After being stored, this data is then being sent to your analytics tool. In Google analytics, the most common type of hits are:
- pageviews
- events
- transactions
- social interactions
How does sampling work in Google Analytics?
Google analytics sets a limit of 10 millions of hits per month per property. It is also important to understand that each view associated with a property will create a set of unsampled, pre-aggregated data tables, which are processed on a daily basis. Concretely, this means that standard reports such as audience, all traffic or content reports overview will remain unsampled.
But very often, these standard reports are not satisfying for google analytics users. For instance, you might need to filter some sets of data to find the bucket of users that generate the majority of your revenue. This is when you do an ad-hoc request to Google Analytics and that your data might get sampled. The most common actions leading to sampling are the following:
- adding a secondary dimension
- applying a filter
- applying a specific segment
- creating a custom report
Let’s take a concrete example.
In the first snapshot below, I took the all traffic report over the last 3 months of a Semetis client. As you can see, data is unsampled and report is based on 100% of sessions.
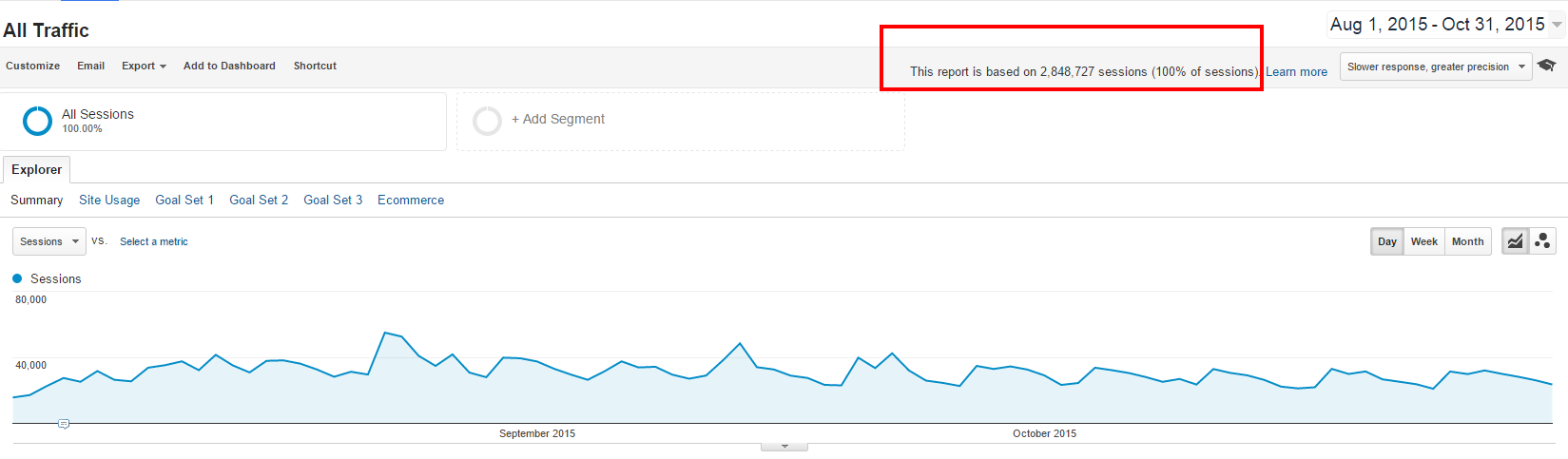
In the second one, I apply a segment to the same report to isolate mobile traffic. Now, the report is only based on 14% of sessions and thus sampled.
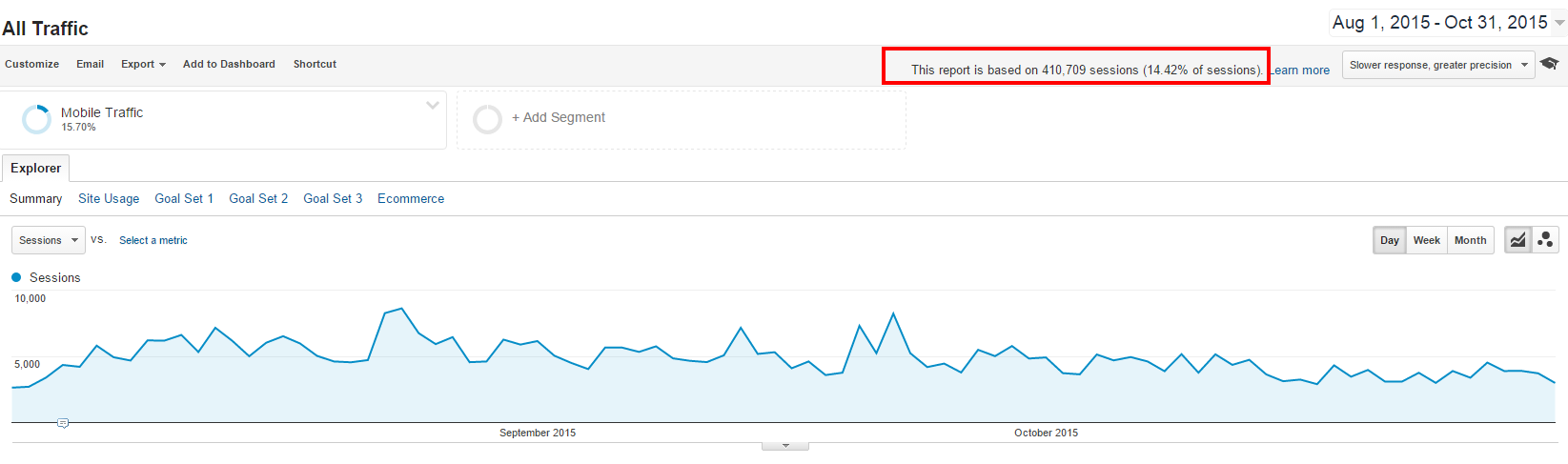
Sampling as such is not a bad thing if you can still rely your observations on a substantial amount of data (70% to 90%). On the other side, below 10%, this can be dangerous and lead to misinterpretation and bad conclusions.
Is there a workaround?
Solution 1: Adapt your date range
When you need to look at long time range (over a year), try to change it to a lower period, for instance month by month. You can then use excel or a spreadsheet to aggregate all the data.
Solution 2: Work with Google Analytics API
Another possible solution is to use the GA API when you can configure precisely the data and time range you want (for instance every day) and retreat them with spreadsheets. Keep in mind that requests to the API are limited to 50.000 hits per day and 10.000 rows per request.
Solution 3: Switch to Google Analytics Premium
If you constantly get sampled data, you may want to consider Google Analytics Premium. One of the advantages of premium is that it can process up to 20 billion of hits and you can export up to 3.000.000 of rows per request. The good new is that Semetis is Google Premium official reseller. So do not hesitate to contact us.
Author: Stéphane Juricic